|
L-ORNITHINE HYDROCHLORIDE |
| Synonyms. L-(+)-2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid hydrochloride; L-Ornithine Hydrochloride; (S)-2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid monohydrochloride; (S)-(+)-2,5-Diaminopentanoic acid hydrochloride; L-2,5-Diaminovaleric acid; Other RN: 68274-41-9 |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
3184-13-2 |
|
EINECS RN |
221-678-6 |
|
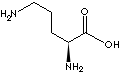
FORMULA |
H2N(CH2)3CH(NH2)COOH·HCl |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
168.62 |
|
H.S CODE |
2922.49.3800 |
|
SMILES |
NCCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O.Cl |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Amino Acid |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Ornithine is a central part of the urea cycle, which allows for the disposal of excess nitrogen. |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
White to off-white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
245 C (Decomposes) |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
1.57 |
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
543 g/l at 20 C |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | Soluble in mineral acids |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. Moisture and light sensitive |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Instability: 0; |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Wikipedia Linking - Ornithine PubChem Compound Summary - L-Ornithine KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - L-Ornithine http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - L-Ornithine http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - L-Ornithine Local
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
White to off-white crystalline powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
+22° ~ +25° (C=4 in 6 N HCl) |
|
Fe |
10ppm max |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|
As |
2ppm max |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
Not regulated |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
May cause eye and skin irritation. May cause respiratory and digestive tract irritation. Target Organs: No data found. |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
Warning |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H319 |
|
P STATEMENTS |
P305 + P351 + P338 |
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
36 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26 |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|